Java简单的输入输出流
从键盘输入
读取变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
| public class HDU_4957 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in); int tt=s.nextInt(); System.out.println(tt); } }
|
流读取
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
| import java.io.*; public class test{ public static void main(String args[]) { mb_echo(System.in); } public static void mb_echo(InputStream in) { try { while (true) { int i = in.read(); if (i == -1) return; char c = (char) i; System.out.print(c); } } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println(e); } System.out.println(); } }
|
字节数组读取法。
1 2 3 4 5 6
| int n = in.available(); if (n > 0){ byte[ ] b = new byte[n]; if (in.read(b) == -1) return; }
|
重新定位到已有文件作为输入
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
| import java.io.*; public class Test1{ public static void main(String args[]) { try { System.setIn(new FileInputStream("文件地址+test.txt")); } catch (FileNotFoundException ex) { System.out.println(ex); return; } test.mb_echo(System.in); } }
|
Java读写文件流
字节流读写文件
字节流写文件
将十个数字(0-9)写到文件“test.txt”中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
| import java.io.*; public class test6{ public static void main(String args[]){ int i; byte[] b=new byte[10]; try{ FileOutputStream f =new FileOutputStream("test.txt"); for (i=0;i<10;i++) b[i]=(byte)(48+i); f.write(b); f.close(); } catch(Exception e){ System.out.println(e); } } }
|
字节流读文件
运用FileInputStream编写程序,输出文件“test.txt”的内容,并统计文件的大小(字节数)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
| import java.io.*; public class test5{ public static void main(String args[]){ int i; int b; try{ FileInputStream f =new FileInputStream("test.txt"); for (i=0; (b=f.read())!=-1; i++) System.out.print((char)b); System.out.println(); System.out.println("TOTAL="+i); f.close(); } catch(Exception e){ System.out.println(e); } } }
|
字符流读写文件
字符流和字节流本质上是一样的,不过字符流以字符大小为单位读写文件
使用的方法是:
1 2 3 4 5
| FileReader in = new FileReader("in.txt"); FileWriter out = new FileWriter("out.txt"); int c; c=in.read(); out.write(c);
|
诸如此类的。
句柄读文件
这个方法适用于读大型文件,利用缓冲减少读取次数,可以提高效率。
1
| BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(args[i]));
|
随机读写文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
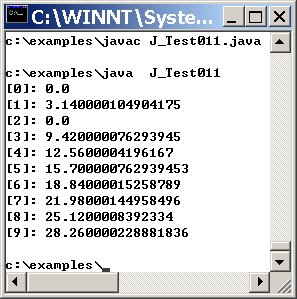
| import java.io.*; class Test11{ public static void main(String args[]){ try{ RandomAccessFile f =new RandomAccessFile("test.txt","rw"); int i; double d; for (i= 0; i< 10; i++) f.writeDouble(3.14f*i); f.seek(16); f.writeDouble(0); f.seek(0); for (i= 0; i< 10; i++){ d=f.readDouble(); System.out.println("["+i+"]: "+d); } f.close(); } catch (IOException io){ System.out.println(io); System.exit(-1); } } }
|
效果如下:
基本数据类型的文件读写
写文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
| import java.io.*; class J_Test8{ public static void main(String args[]){ int i=10; double k=3.1413; char c='x'; boolean fl=true; try{ DataOutputStream f =new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("out.txt")); f.writeInt(i); f.writeDouble(k); f.writeChar(c); f.writeBoolean(fl); f.close(); } catch(Exception e){ System.out.println(e); } } }
|
读文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
| import java.io.*; class J_Test8{ public static void main(String args[]){ int i; double k; char c; boolean fl; try{ FileInputStream inputFile= new FileInputStream("out.txt"); DataInputStream in =new DataInputStream(inputFile); i=in.readInt(); k=in.readDouble(); c=in.readChar(); fl=in.raedBoolean(); f.close(); System.out.println("i="+i); System.out.println("k="+k); System.out.println("c="+c); System.out.println("fl="+fl); } catch(Exception e){ System.out.println(e); } } }
|
工作路径
注意,txt文件要(会)放在根目录下,具体用以下代码查看你的根目录
1
| System.out.println("用户的当前工作目录:/n"+System.getProperty("user.dir"));
|
文件类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
| import java.io.*; class Test015{ public static void main(String args[]){ for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++){ File f = new File(args[i]); if (f.exists()){ System.out.println("getName: " + f.getName()); System.out.println("getPath: " + f.getPath()); System.out.println("getAbsolutePath: " + f.getAbsolutePath()); System.out.println("getParent: " + f.getParent()); if (f.canWrite()) System.out.println(f.getName() + " is writable."); if (f.canRead()) System.out.println(f.getName() + " is readable."); if (f.isFile()) System.out.println(f.getName() + " is a file."); else if (f.isDirectory()) System.out.println(f.getName() + " is a directory."); else System.out.println("What is this?"); if (f.isAbsolute()) System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath()+ " is an absolute path."); else System.out.println(f.getName() + " is not an absolute path."); System.out.println("Last Modified: " + f.lastModified()); System.out.println(f.getName() + " is " + f.length() + " bytes."); } else System.out.println("I'm sorry. I can't find the file " + args[i]); } } }
|