描述
本福特定律,也称为本福特法則,说明一堆从实际生活得出的数据中,以1为首位数字的数的出现概率约为总数的三成,接近期望值1/9的3倍。推广来说,越大的数,以它为首几位的数出现的概率就越低。它可用于检查各种数据是否有造假。
解释
本福特定律说明在 {\displaystyle b} b进位制中,以数 n起头的数出现的概率为 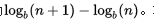 。本福特定律不但适用于个位数字,连多位的数也可用。
。本福特定律不但适用于个位数字,连多位的数也可用。
在十进制首位数字的出现概率(%,小数点后一个位):
| 数 |
概率 |
| 1 |
30.1% |
| 2 |
17.6% |
| 3 |
12.5% |
| 4 |
9.7% |
| 5 |
7.9% |
| 6 |
6.7% |
| 7 |
5.8% |
| 8 |
5.1% |
| 9 |
4.6% |
题意
给定n,b,q。对于无限长数列的a[],ai = b*q^i。问n是ai的前缀的概率。
AC代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
| #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <map> using namespace std; #define ll long long #define mod 2147483647 #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f int main() { int T,ca=0; for(cin>>T;T--;){ int n,b,q; scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&b,&q); double ans; if (q==10||q==100||q==1000){ if (b==n||b/10==n||b/100==n||b/1000==n||b*10==n||b*100==n||b*1000==n) ans=1; else ans=0; } else{ if (q==1){ if (b==n||b/10==n||b/100==n||b/1000==n) ans=1; else ans=0; } else ans=log10((double)(n+1)/double(n)); } printf("Case #%d: %.5f\n",++ca,ans); } return 0; }
|
。本福特定律不但适用于个位数字,连多位的数也可用。